The larger aim of 100 GW power generation from solar PV under the national mission has entered on its crucial third and final phase. Authorities devise novel ways and methods of capacity added to the national grid, during the balance mission period.
Broadly, the plan was to achieve the objectives through two classifications namely Roof Top Solar and Ground-mounted systems. The predictions are not favouring a success under rooftop number. Therefore, new models are foreseen to meet RE share on grid capacity.
Largely, three potential groups have emerged stronger. We will examine the projected contribution by these sources in the national energy mix.
Floating Solar Photo Voltaics (FSPV):
The foremost among the 'new generation' PV generator is Floating Solar PV. Hydro reservoirs are the targeted substitutes for land use. The floats, upon which Module mounting structure and PV modules are fixed, shall be materials combining various strengths:
a. Buoyancy factor
b. Compatibility with drinking water carriage requirements.
c. Long aquatic life period
Solar PV modules are expected to deliver additional 10-15% energy due to its ‘cool’ bottom. This extra energy would compensate the additional cost for the floats
Besides, the float coverage on water bodies curtails water evaporation considerably. Algae in water also do not find its growth under the covered surface. Most of the hydro reservoirs for irrigation are located in the tailrace of large Hydro generators. This ensures extra power generating capacity for the utility. In India, an estimated potential of 900 GW is seen from the reservoirs of large dams in India.
Soura Natural Energy Systems India is a proud partner in the construction of country's largest floating plant at Banasura Sagar dam in Wayanad District of Kerala. The plant with a capacity of 500 kW was put on service during December 2017 as a pilot project by Kerala State Electricity Board, the utility giant of the state.
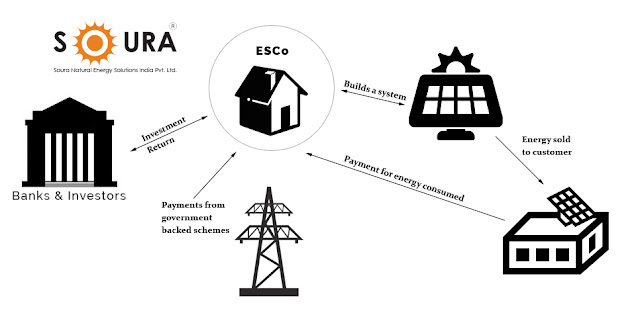
Renewable Energy Service Company (RESCO) Model:
Under the RESCO model, the consumer can install a solar power plant without making upfront investments. A PPA is signed between RESCO and consumer, at a mutually agreed price. RESCO will set up the plant and then monetise the energy produced.
RESCO models are not yet practised much in our country. National level bidding by SECI indicates the strong presence of rental market space in Solar RT sector. A programme under RESCO model shall be introduced, targeting large Industries.
Soura Natural Energy is a key player for RESCO model in the State of Kerala. With many orders under execution including a Utility scale RESCO project, Soura is racing towards its target of 800 MW allotted by Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI).
Micro Grid Model:
The emergence of Microgrid-as-a-Service (MaaS) model for energy challenges is being acknowledged globally. RT Solar only provides energy self-sufficiency, while, Microgrids can accelerate social development.
The government of India is expected to firm up a policy on Microgrids by end of 2017. Microgrid development across India is likely to be core to achieving targets under NSM. A pilot programme is being implemented by Jharkhand Renewable Energy Development Agency (JREDA) to electrify 320 households across 11 villages through the development of Microgrids. The works also include turnkey implementation of decentralized distributed SPV power plants along with Power Distribution networks to unelectrified households. Microgrid projects are also attempted in Bihar and UP. Microgrid would also lead distributed energy investments for us. Such innovative business models bring radical changes in Industry.
Soura Natural Energy looks forward its first Microgrid model business by this year through its Branch office in Ranchi, State of Jharkhand.
For More Details: Soura Natural Energy Solutions


solar resco installation, solar resco model
ReplyDelete